◆ Current Causes and Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
In general, liver cancer, like other liver diseases, is not prone to symptoms in the early stage. Once obvious subjective symptoms appear, the condition is usually not slight. The symptoms of liver cancer are related to the size and location of the tumor, which is also one of the important keys that liver cancer has always ranked first among the top ten causes of cancer death in the country. Like other cancers, the causes of liver cancer are very complex and rarely results from a single cause. Most scholars believe that hepatitis B and hepatitis C are the main causes of liver cancer, followed by procedures of development (such as liver cell necrosis), which progresses to the stage of liver cirrhosis and cell canceration, and finally resulting in liver cancer that can be detected clinically.
Liver cancer is a malignant cancer, with an average age of onset of about 50-60 years old. If there is no effective treatment, from the appearance of symptoms to death, it generally takes only 4 to 6 months. Early clinical detection of liver cancer is the key to successful treatment. As liver cancer tumors can usually be treated by surgery in its early stages, according to statistics, the survival rate of liver cancer below three centimeters after surgery is about 40%, and if the liver cancer is below two centimeters, the survival rate of ten years after surgery can reach 80%.
The initial diagnosis of liver cancer is mainly ultrasound and fetal protein (AFP) examination. 85% of patients with large liver cancer will have higher fetal protein levels, but for small liver cancers less than 3 cm, only about 2/3 of patients will have increased fetal protein levels. Therefore, if the fetal protein value is normal, it cannot be determined that there is no liver cancer. Abdominal ultrasound can detect whether the liver has nodules or tumors. Abdominal ultrasound examinations are very sensitive to liver cancer, and can locate tumors about 1 cm. However, fatty liver, commonly known as “oil wrapped in liver,” can make the liver look white; too much gas in the intestines, uneven liver surface, obscurity caused by bones, or conditions in which the tumor is too hidden can also be factors that interfere with the physician’s interpretation.
Computed tomography (CT) or nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI) examinations can provide further information on the nature of liver tumors and are currently used as a tool for the diagnosis of liver cancer. There are about 3 million people with chronic hepatitis B and C in Taiwan. When hepatitis continues to worsen, it would lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. At present, the precise examination of liver cancer is mainly based on computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. If the tumor size is 1 to 2 cm, the accuracy of computer tomography is 60%, and the accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging is as high as 80 to 90%. However, when the tumor is 1 cm, the accuracy of computer tomography decreases only to 10%, while that of magnetic resonance imaging also drops to 30% to 70%. For liver cirrhosis patients carrying hepatitis B and C, due to liver cirrhosis, the liver becomes uneven, it is more difficult for to detect liver cancer lesions with ultrasound and general MRI. Doctors recommends that when these patients undergo their annual MRI examinations, they should use liver-targeted imaging agent as its sensitivity to tumors is as high as 90%. Liver-targeted imaging agents can detect early small liver cancers which are less than one centimeter, and early detection can improve the cure rate of patients.
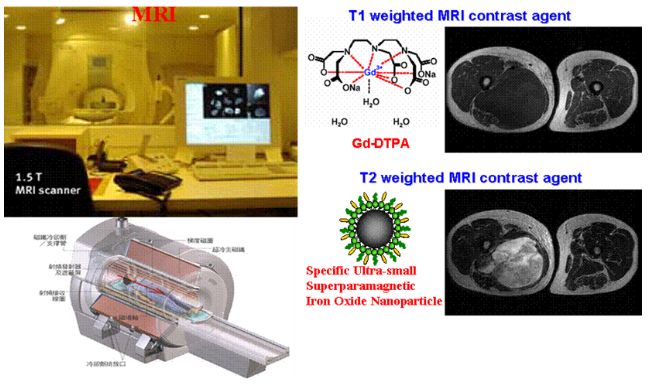
However, in the diagnosis of liver tumors, it is usually necessary to inject a gadolinium contrast agent to distinguish benign or malignant tumors. Traditionally, the linear chelating agent gadolinium-based contrast agent can take advantage of its rapid in-and-out characteristics in blood vessels to enhance the image clarity of liver tissue, yet it is not specific for liver tumors. At present, only the developer approved by FDA in 2008, Primovist (Gd-EOB-DTPA), can effectively diagnose liver cancer.
However, in the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) in July 2017, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has proposed to suspend market authorization on four linear gadolinium imaging agents regarding the gadolinium imaging agents us ed in clinical MRI examinations. Currently, Primovist® is an existing linear gadolinium product that can be used for liver cancer imaging on the market. According to animal experiments of IOP Injections, it can effectively distinguish hemangiomas and tumors, and the accuracy of determination is high in the range of 0.1mm~0.5mm. Therefore, IOP Injection has the opportunity to be an effective basis for liver tumor judgment.
◆ MPB-1523's Innovative Appeals:
MPB-1523 (IOP Injection) are iron oxide nanoparticles modified with polyethylene oxide, possessing characteristics of high nuclear magnetic relaxation and high efficiency of macrophage phagocytosis. After macrophages phagocytose superparamagnetic iron oxide particles, related regional signals would be reduced, while the tumor tissues signals remain unchanged as they do not contain normal phagocytic cells, so a signal contrast is generated. This feature can be applied to the visualization of tissues and organs rich in reticuloendothelial cells, such as the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes for medical personnel to judge whether the patient has a benign or malignant tumor and whether lymphatic metastasis occurs, thus providing the following advantages:
- Benign hemangioma and malignant tumors can be accurately identified
- There would be no suspicions on whether heavy metals such as gadolinium remain in the body.
◆ Clinical progress of MPB-1523:
The Phase I clinical trial has been completed at Taipei Veterans General Hospital. The Phase II clinical trial has completed the recruitment of the patients in the Taiwan in 2020Q3.
◆ Inquiries about related clinical trials
For more information, please go to http://www1.cde.org.tw/ct_taiwan/archive1.html and search for the keyword “巨生”
or https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/home ,and search for the keyword “MegaPro” in Other Term.